Conjunctivitis: Causes, Symptoms, Types, and Treatment Options
Introduction:
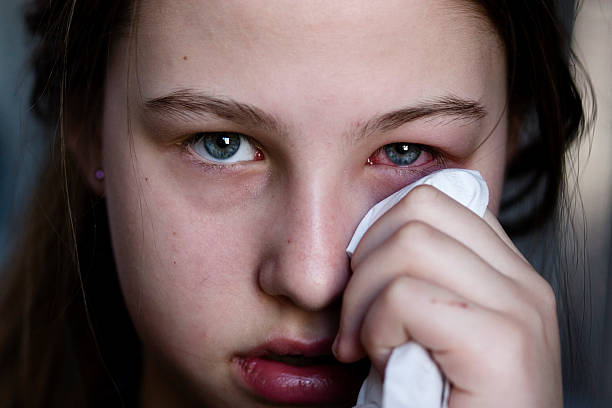
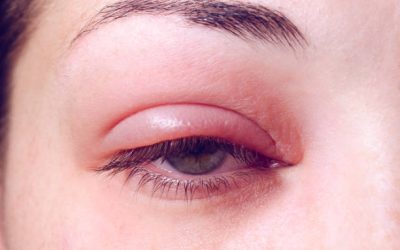
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye, is a common eye condition characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelids. It can affect people of all ages and is highly contagious. This article will discuss the causes, symptoms, types, and treatment options for conjunctivitis.
Causes of Conjunctivitis:
Conjunctivitis can have various causes, including:
- Viral Infection: Viral conjunctivitis is the most common form of pink eye and is highly contagious. It spreads through contact with infected individuals or surfaces. Viruses such as adenoviruses and herpes simplex can cause this type of conjunctivitis.
- Bacterial Infection: Bacterial conjunctivitis can occur when bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumonia, infect the eyes. It is contagious and easily spreads through direct contact.
- Allergic Reaction: Allergic conjunctivitis is triggered by allergies to substances like pollen, dust mites, or certain medications. It is not contagious and often affects both eyes.
- Chemical Irritants: Exposure to irritants like chlorine, smoke, or harsh chemicals can lead to chemical conjunctivitis. This type of conjunctivitis is not contagious and usually affects only one eye.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis:
Conjunctivitis symptoms can vary based on the cause, but common symptoms include:
- Redness in the whites of the eyes
- Itching or a burning sensation in the eyes
- Excessive tearing or watery discharge
- Gritty or sandy feeling in the eyes
- Swollen eyelids
- Sensitivity to light
- Crusting or stickiness around the eyes, especially after sleep
Types of Conjunctivitis:
There are three main types of conjunctivitis:
- Viral Conjunctivitis: This form of conjunctivitis is highly contagious and usually starts in one eye before spreading to the other. It typically causes a watery discharge and can be accompanied by other cold-like symptoms.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Bacterial conjunctivitis often leads to a thick, yellow or greenish discharge. It can affect one or both eyes and is highly contagious.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Allergic conjunctivitis is not contagious and is typically associated with itching, redness, and excessive tearing. It often occurs alongside other allergic symptoms like sneezing or a runny nose.
Treatment Options for Conjunctivitis:
The treatment of conjunctivitis depends on its cause:
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Viral conjunctivitis tends to resolve on its own within one to two weeks. Applying a warm compress to the eyes, using artificial tears for lubrication, and practicing good hygiene by avoiding touching the eyes or sharing personal items can help alleviate symptoms and prevent the spread of infection.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Bacterial conjunctivitis is often treated with antibiotic eye drops or ointments prescribed by a healthcare professional. It’s important to complete the full course of antibiotics as directed to ensure the infection is eradicated.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: Avoiding allergens, such as pollen or pet dander, can help minimize the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis. Additionally, over-the-counter antihistamine eye drops or oral antihistamines may be recommended to reduce itching and inflammation.
In all cases of conjunctivitis, maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial to prevent the spread of infection. This includes frequently washing hands, avoiding touching the eyes, and thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting items like towels or contact lenses.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
While most cases of conjunctivitis can be managed at home, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional if:
- Symptoms worsen or do not improve within a few days
- Vision is affected or there is severe eye pain
- There is pus-like discharge or eyelids become stuck together
- There is a history of recent eye injury or foreign body in the eye
Conclusion:
Conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is a common eye condition that can have different causes, including viral or bacterial infections, allergies, or exposure to irritants. Its symptoms vary but often include redness, itching, and discharge. Treatment options range from self-care measures to prescription medications, depending on the underlying cause. Practicing good hygiene and seeking medical attention when necessary can help manage conjunctivitis effectively.