Blepharitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction:
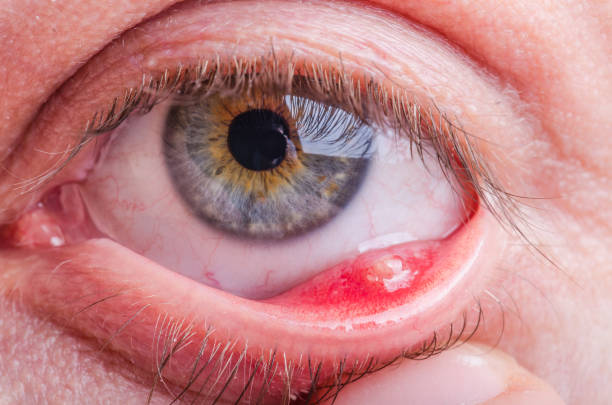
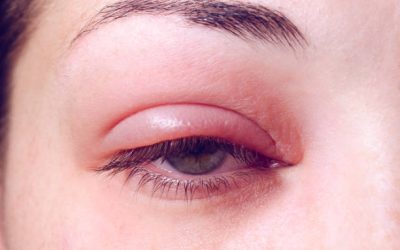
Blepharitis refers to the inflammation of the eyelids, which causes redness, itching, and soreness. It is a common and persistent condition that can affect people of all ages. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for blepharitis.
Causes of Blepharitis:
Several factors can contribute to the development of blepharitis. One common cause is the overgrowth of bacteria on the eyelids. This can occur when the oil glands located near the base of the eyelashes become clogged, leading to the accumulation of bacteria and debris. It is a buildup of oil and debris on the eyelids and eyelashes. Additionally, Complicated skin conditions such as seborrheic dermatitis and rosacea can also contribute to the development of blepharitis. Furthermore, Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) also has caused Blepharitis eye conditions in many. It is one of the common reasons to cancel (elective) planned surgery.
Symptoms of Blepharitis:
The symptoms of blepharitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
- Redness and swelling of the eyelids
- Itchy, sore, or burning sensation in the eyes or red eyelids that stick together
- Crusty debris along the eyelashes
- Sensitivity to light
- Watery or dry eyes
- Flaking or scaling of the skin around the eyelids
- Sticking or crusting of the eyelids in the morning
- Blurred vision
- Visible dandruff on your eyelashes
Types of Blepharitis
There are two main types of blepharitis; Anterior Blepharitis and Posterior Blepharitis
Anterior Blepharitis:
This occurs when the inflammation affects the skin at the base of your eyelashes
Posterior Blepharitis:
This occurs when the inflammation affects your eyelid gland. Meibomian Gland dysfunction (MGD) can happen when the eyelid gland becomes clogged. Sometimes people experience the two types of blepharitis because the causes are often connected.
Diagnosing Blepharitis:
To diagnose blepharitis, an eye care professional will typically perform a thorough examination of the patient’s eyes and eyelids. They may also use specialized instruments to assess the quality and quantity of tears produced by the patient’s eyes. In some cases, further tests such as a swab culture or a biopsy may be performed to determine the underlying cause of the condition.
Treatment Options for Blepharitis:
The treatment of blepharitis usually involves a combination of self-care measures and medical interventions. Some common treatment options include:
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected eyelids can help reduce inflammation and loosen crusts. This can be done by soaking a clean washcloth in warm water and placing it over the closed eyelids for several minutes.
- Eyelid Hygiene: Regularly cleaning the eyelids can help remove debris and minimize bacterial overgrowth. This can be done by using a gentle eyelid cleanser or baby shampoo diluted with warm water. Using a clean cotton swab, the eyelid margins can be gently scrubbed in a back-and-forth motion.
- Medications: In some cases, eye drops or ointments may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation. This can include antibiotics to target bacterial overgrowth or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. Additionally, artificial tears or lubricating eye drops may be recommended to relieve dryness.
- Supplements: Eye care professionals recommend a diet rich in Omega 3 fatty acids or the use of nutritional supplements to help manage Blepharitis. Increasing the consumption of Omega 3 Fatty acids can help to improve the oil in your glands and relieve symptoms associated with Blepharitis, MGD, and Dry Eye.
- Hydrate: Eye care professionals recommend the use of preservatives-free eye lubricants and sprays which are more effective than preserved eyedrops or ointments in reducing inflammation in the eyes. Tear replacement of eyedrops, spray, or ointments is traditionally considered a mainstay of Blepharitis management, however, it is recommended that these are used with other therapies to target the underlying cause of Blepharitis.
- Management of underlying conditions: If blepharitis is caused by an underlying skin disorder such as seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea, treating the skin condition can help manage blepharitis symptoms. This may involve the use of topical or oral medications prescribed by a dermatologist.
Preventing Blepharitis:
While some cases of blepharitis cannot be prevented, there are certain measures that individuals can take to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These include:
- Practicing good eyelid hygiene: Regularly cleaning the eyelids can help prevent bacterial overgrowth and minimize inflammation.
- Avoid eye makeup and contact lenses during flare-ups: These can exacerbate symptoms and increase the likelihood of developing an infection.
- Avoid rubbing or touching the eyes: This can further irritate the eyelids and worsen inflammation.
- Protecting the eyes from irritants: Wearing glasses or goggles in dusty or windy environments can help prevent debris from irritating the eyes.
Conclusion:
Blepharitis is a common and chronic condition that causes inflammation of the eyelids. While it can be persistent, it is manageable with proper treatment and self-care measures. If you experience any symptoms associated with blepharitis, it is important to consult an eye care professional for diagnosis and guidance on the appropriate treatment approach.