Introduction
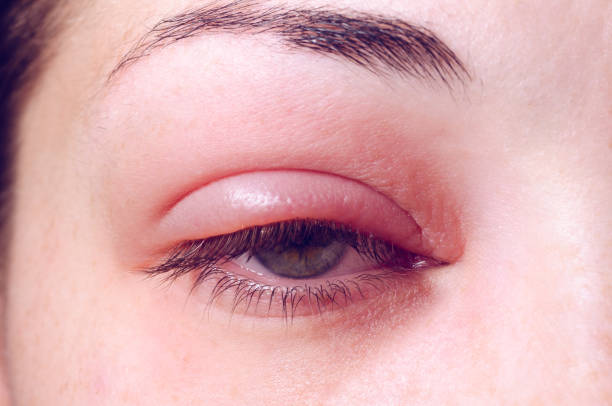
A chalazion is a common eyelid condition characterized by the development of a painless, firm lump due to inflammation and blockage of the oil gland. It typically affects the Meibomian glands, which are located in the eyelids and produce the oily component of tears. When one of these glands becomes blocked, the oil cannot flow properly, leading to the formation of a chalazion.
Causes:
The exact cause of chalazion is not always known, but some common factors can contribute to its development. These include:
- Blockage of the Meibomian glands: This can occur due to thickened oils or debris getting trapped in the gland.
- Inflammation: Inflammation of the eyelids or surrounding tissues can lead to the blockage of the oil gland.
- Blepharitis: A chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelids, which can increase the risk of chalazion.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormonal levels, such as those seen during puberty or pregnancy, can contribute to the development of chalazion.
Symptoms:
Chalazia typically presents as a painless, firm lump on the eyelid, usually on the inner part (towards the nose). Other common symptoms include:
- Swelling and redness of the eyelid.
- Tenderness or sensitivity to touch.
- Blurred vision in rare cases when the chalazion puts pressure on the eye.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing a chalazion is usually done through a physical examination by an eye care professional. They will examine the affected eyelid and may ask questions about your symptoms and medical history. In some cases, they may also perform additional tests, such as eyelid eversion, to evaluate the extent of the condition.
Treatment:
Treatment options for chalazion depend on the severity and persistence of symptoms. Mild chalazia often resolves on their own without treatment. However, the following interventions can help speed up healing and alleviate discomfort:
- Warm compresses: Apply a warm compress to the affected eyelid for 10-15 minutes, several times a day. This helps to soften the oil, promote drainage, and reduce inflammation.
- Gentle massage: After applying a warm compress, gently massage the affected area with clean fingers. This can help in the movement of the blocked oil and aid in drainage.
- Eyelid hygiene: Maintain proper eyelid hygiene by washing your eyelids gently with warm water and mild soap or using over-the-counter eyelid cleansers.
- Medications: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe antibiotic ointments or eye drops to prevent infection and reduce inflammation.
- Steroid injections: For larger or persistent chalazia, a doctor may administer a corticosteroid injection directly into the lump to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Surgical drainage: If the chalazion does not respond to conservative measures or if it is causing significant discomfort or vision problems, surgical drainage may be performed. This procedure involves making an incision and draining the contents of the chalazion.
Conclusion
Chalazion is a common eyelid condition that can cause discomfort but it is usually not serious. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for chalazion can help individuals manage this condition effectively. It is important to consult with an eye care professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for chalazion. They can provide personalized recommendations based on the severity and characteristics of your condition.